Omaha is poker taken to the power level. With four cards in hand and the ability to make a combination of two of your own and three community cards, the game becomes much more dynamic and complex than traditional Hold’em. But don’t be scared! In this guide, we will analyze the basic strategies that will help you master Omaha.
Why use strategies in Omaha
What makes Omaha unique is that each player receives four cards, which means there are significantly more possible combinations and strategies than in Texas Hold’em. Participants must understand how to take advantage of the chance to play the cards most effectively and minimize risk.

Without clear tactics, even the strongest combinations will not bring the desired win. For example, in a game against experienced opponents, it is important not only to know what cards are in hand, but also to understand what combinations can arise on the flop, turn and river. Strategy allows you to build a game plan for Omaha and anticipate the actions of opponents, rather than react to the situation after the fact.
How to Build a Proper Strategy
There are many factors to consider when implementing a winning Omaha strategy, from choosing starting hands to managing your bets wisely. The best hands in Omaha include pairs of aces with high connecting cards. Professionals often choose aggressive tactics to force opponents to open up and make mistakes.
Proper positioning also plays an important role. The later you take a seat at the table, the more information you will have about your opponents’ actions, and the easier it is to adjust your strategy. Use this advantage to dominate.
Basic Mistakes in Omaha
A mistake is not always a bad decision, sometimes it is simply a consequence of insufficient analysis of the situation. When choosing a strategy in Omaha, it often happens that you overestimate the strength of your hand, especially when cards that seem strong on the flop, but do not provide a real advantage. For example, having two pairs on the flop may look impressive, but without the prospect of improving on the turn or river, such combinations become vulnerable.
Key points:
- Overestimating the strength of starting hands. Players often see strong starting hands, such as double pairs, and begin to aggressively raise bets without assessing the potential risks from opponents who can collect straights or flushes.
- Underestimating the capabilities of the opponent. Players forget that in Omaha each opponent has four cards, which increases the number of potential combinations. For example, on a board with two suited cards, there is a high probability that one of the opponents will collect a flush.
- Trying to keep the bets low instead of aggression. When aggression is required to protect a hand or seize the initiative, many players prefer to simply check, which gives opponents the opportunity to improve their hands for free. For example, on the turn, an aggressive bet could force an opponent to fold, but passive tactics lead to unexpected losses.
The best way to avoid mistakes is to constantly analyze the actions of all participants, take into account the probabilities of combinations and not be afraid of aggressive actions when the situation calls for it. It is also important to monitor your emotions and not let your first success influence your future decisions.
How to Win at Omaha: Secret Techniques, Strategies
 To win, you need to have a deep understanding of the game and use secret techniques that give you a real advantage. One of these is an aggressive strategy on the flop. According to statistics, players who raise on the flop increase their chances of winning by 25%. This approach allows you to seize the initiative and make your opponents doubt their actions.
To win, you need to have a deep understanding of the game and use secret techniques that give you a real advantage. One of these is an aggressive strategy on the flop. According to statistics, players who raise on the flop increase their chances of winning by 25%. This approach allows you to seize the initiative and make your opponents doubt their actions.
It is also important to monitor the dynamics of bets and the behavior of opponents on the turn and river. Research shows that with a sharp increase in amounts on the turn, the probability of bluffing is about 35%. It is important to be able to interpret these signals and draw the right conclusions.
It is also critical to consider the pot odds in Omaha. If the current one is $1,000 and the bet is $200, the pot odds are 5 to 1. This means that you need to win at least one of six hands for this amount to be justified.
Analysis of past hands shows that professionals often bet 75% of the pot on the turn to limit their opponent’s range and force them to make a mistake. Cool-headedness and the ability to assess risks at each stage are the main differences between successful players and beginners.
Choosing bets: risk or stability?
Balance between risk and stability. Experienced players know when to raise the amount to knock out opponents, and when it is better to hold back and leave as many opponents in the game as possible to increase the pot. For example, in the early stages it is better to stick to cautious strategies to see more cards, but in the late stage, especially on the turn or river, aggressive play can bring the greatest result.
TOP 3 key techniques for beginners:
- Choose the right starting hands. In Omaha, it is important to choose those hands that have the potential to form strong combinations. Beginners should start with high pairs and connected cards. For example, pairs of aces and connectors like 10-J have a high potential for forming combinations on the flop and subsequent streets.
- Don’t be afraid to bluff, but know your limits. Bluffing is a powerful weapon, but unjustified risks can turn against the participant. Professionals bluff 30% of the time, which helps maintain a balance between aggression and predictability. Beginners should only do this in situations where the probability of success is high enough – for example, if opponents show weakness with their bets.
- Don’t overestimate the strength of the flop. The fact that strong cards fell on the flop does not mean that you have the best deal. Always think a few steps ahead and take into account the actions of other participants. For example, if you have two pairs on the flop, and your opponent has a clear tendency to increase bets, this may signal the presence of a stronger combination, such as a straight or a set. Correctly assessing the strength of your hand relative to the board and your opponent’s actions allows you to avoid unnecessary losses and make the right decision.
When and how to change your strategy in Omaha
Pros know: the same tactics do not work in every session. Sometimes it is necessary to change the approach depending on the actions of your opponents. For example, if your opponents are playing too aggressively, it is wiser to use a more cautious approach and wait for the moment to take advantage of their mistakes. Flexibility in the application of strategies is the basis for success in Omaha.
When you see that the game is starting to move to a stage where aggression brings more damage than benefit, it is worth changing tactics to a less aggressive one. This is especially important in the later stages, when every move matters. Approaches require constant adaptation, since opponents also study all the moves and try to predict them.
Conclusion
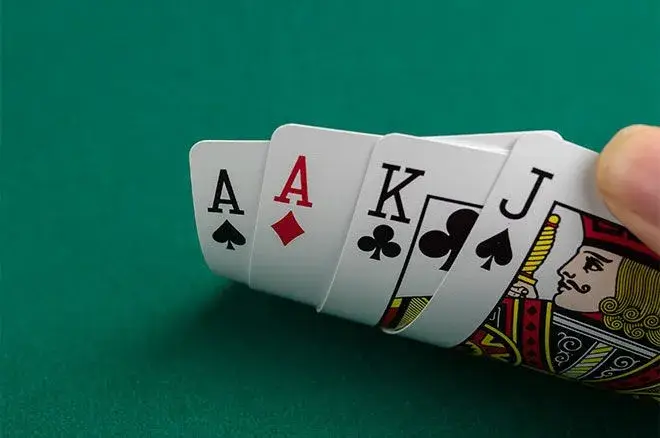 Omaha strategies help to train the right mindset for gambling entertainment. Winning requires a deep understanding of the game, the ability to analyze the situation and react correctly to changes. Constant adaptation and willingness to change your approach is the key to success. Do not be afraid to experiment, learn from your mistakes to make the next games more interesting.
Omaha strategies help to train the right mindset for gambling entertainment. Winning requires a deep understanding of the game, the ability to analyze the situation and react correctly to changes. Constant adaptation and willingness to change your approach is the key to success. Do not be afraid to experiment, learn from your mistakes to make the next games more interesting.

 en
en  de
de  ar
ar  es
es  hi
hi  fr
fr  nl
nl  it
it  pt
pt  el
el 









